-
American History
- American History Honors >
- Unit 0: 1763 - 1800 - Revolutionary America
- Unit 1: 1800 - 1848 - Expansion & Reform
- Unit 2: 1848 - 1877 - A Nation Divided
- Unit 3: 1865 - 1898 - The Gilded Age
- Unit 4: 1890 - 1920 - American World Debut
- Unit 5: 1920 - 1945 - Trials and Tribulations
- Unit 6: 1945 - 1963 - Cold War Tensions
- Unit 7: 1955 - 1980 - Conflicts & Resolutions
- Unit 8: 1980 - present - Modern America
-
World History
- World History Honors
- Unit 1: (1200-1450) - State Building in the Global Tapestry
- Unit 2: (1200-1450) - Networks of Exchange
- Unit 3: (1450-1750) - Land-Based Empires
- Unit 4: (1450-1750) - Sea of Exploration
- Unit 5: (1750-1900) - Revolutions
- Unit 6: (1750-1900) - Imperial Migration
- Unit 7: (1900-present) - Global Conflicts
- Unit 8: (1900-present) - Cold War & Decolonization
- Unit 9: (1900-present) - Globalization
-
Advanced Placement (AP)
-
AP World History
>
- Unit 1: (1200-1450) - State Building in the Global Tapestry
- Unit 2: (1200-1450) - Networks of Exchange
- Unit 3: (1450-1750) - Land-Based Empires
- Unit 4: (1450-1750) - Transoceanic Interconnections
- Unit 5: (1750-1900) - Revolutions
- Unit 6: (1750-1900) - Imperial Migration
- Unit 7: (1900-present) - Global Conflicts
- Unit 8: (1900-present) - Cold War & Decolonization
- Unit 9: (1900-present) - Globalization
-
AP European History
>
- Unit I - The Rise of Europe
- Unit II - Rebirth and Exploration
- Unit III - A Fractured Faith
- Unit IV - A Question of Sovereignty
- Unit V - A Shifting Society
- Unit VI - Revolution
- Unit VII - Political Turmoil
- Unit VIII - Rise of the Nation-State
- Unit IX - Forging the Modern Era
- Unit X - Imperialism and the Great War
- Unit XI - Global Conflicts
- Unit XII - The Long Peace
-
AP World History
>
- Civic Literacy
|
KEY EVENTS
|
The United States takes to the West in pursuit of developing the land gained before the Civil War. From all walks of life come miners, ranchers and farmers willing to confront the challenges of taming the West.
|
|
KEY EVENTS
|
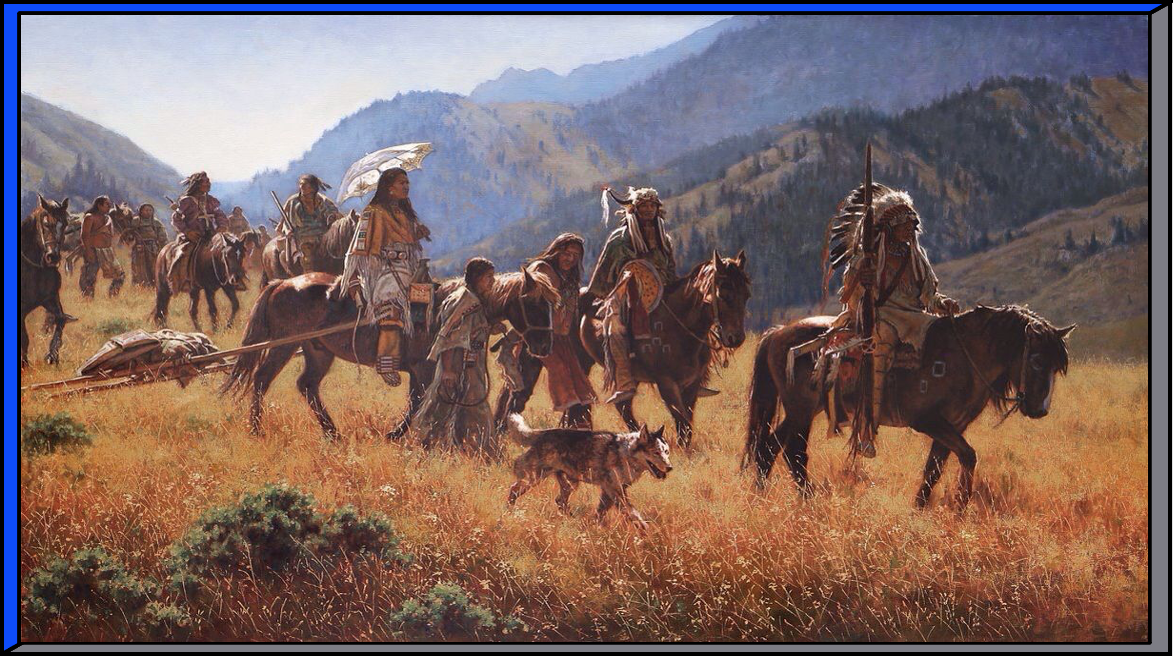
The pressure of white settlers moving into lands held by natives sparks conflict and battles across the West that cause the relationship between the United States and the Indians to deteriorate into a tragic end.
|
|
KEY EVENTS
|
The United States industrialized quickly as America seemed to be entering a Golden Age along with the nations of Europe. From innovations in technology to the innovations of business, America will rise as an industrial power in the world.
|
|
KEY EVENTS
|
Industry grew in the late 1800s as business leaders merged and formed powerful trusts and corporations that dominated the era. However, industrial growth came at a cost as employers took advantage of their laborers. Soon, laborers organized and formed their own groups to fight back and gain rights for themselves.
|
|
KEY EVENTS
|
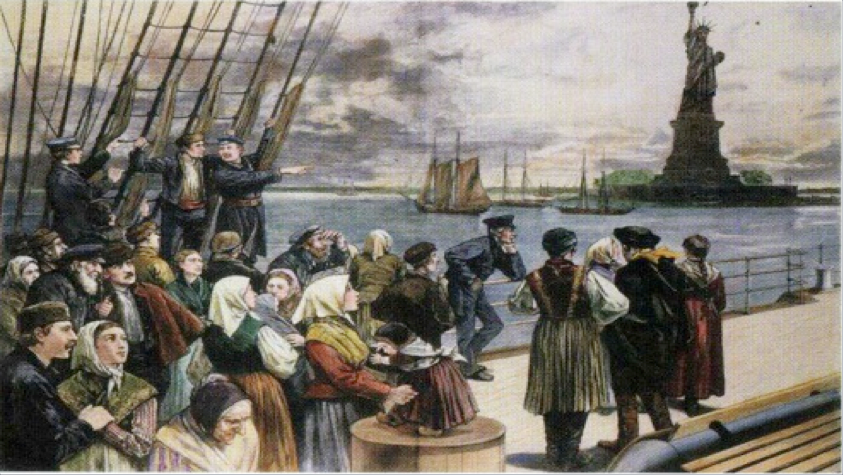
To fully industrialize, America needed a larger work force to work the new factories popping up across the North. After the Civil War, America experienced a large influx of immigrants from Europe and Asia while many farmers migrated to the cities and soon filled the need for a larger work force and therefore, America industrialized quickly.
|
|
KEY EVENTS
|
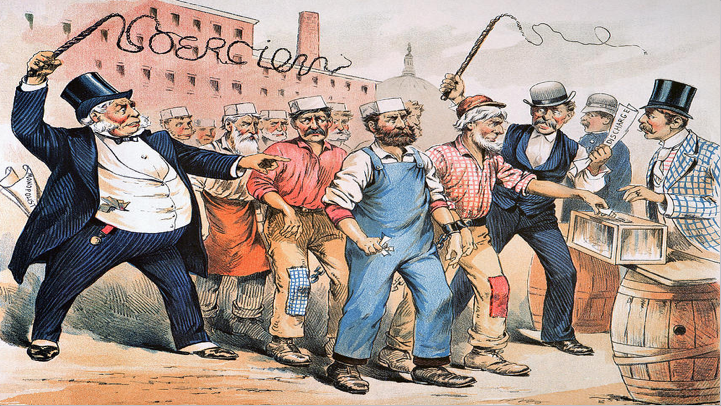
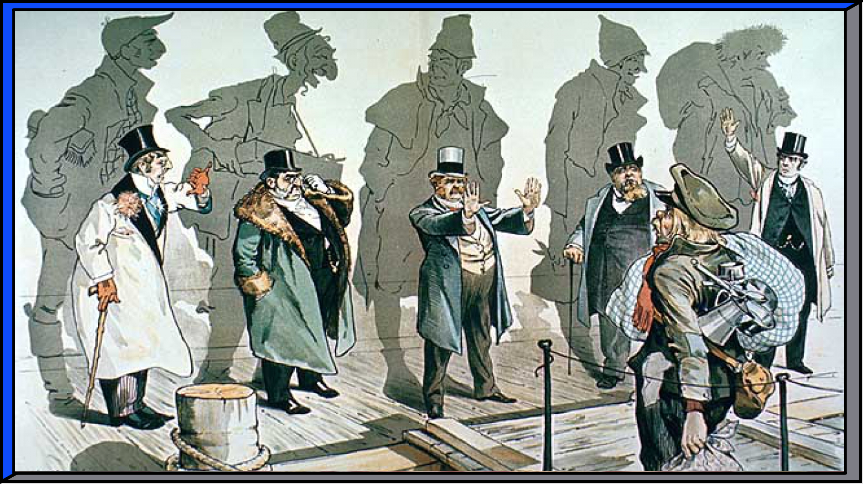
Despite the valuable contributions immigrants made in building America during this period, immigrants often faced hardship and hostility. There was fear and resentment that immigrants would take jobs for lower pay than American workers, and there was prejudice based on religious and cultural differences.
|
|
KEY EVENTS
|
The rapid industrialization of America not only changed the urban landscape of America’s cities but changed the social structure that existed for centuries forming a new middle class with a new market to spend excess money on and changing well established gender roles.
|
|
KEY EVENTS
|
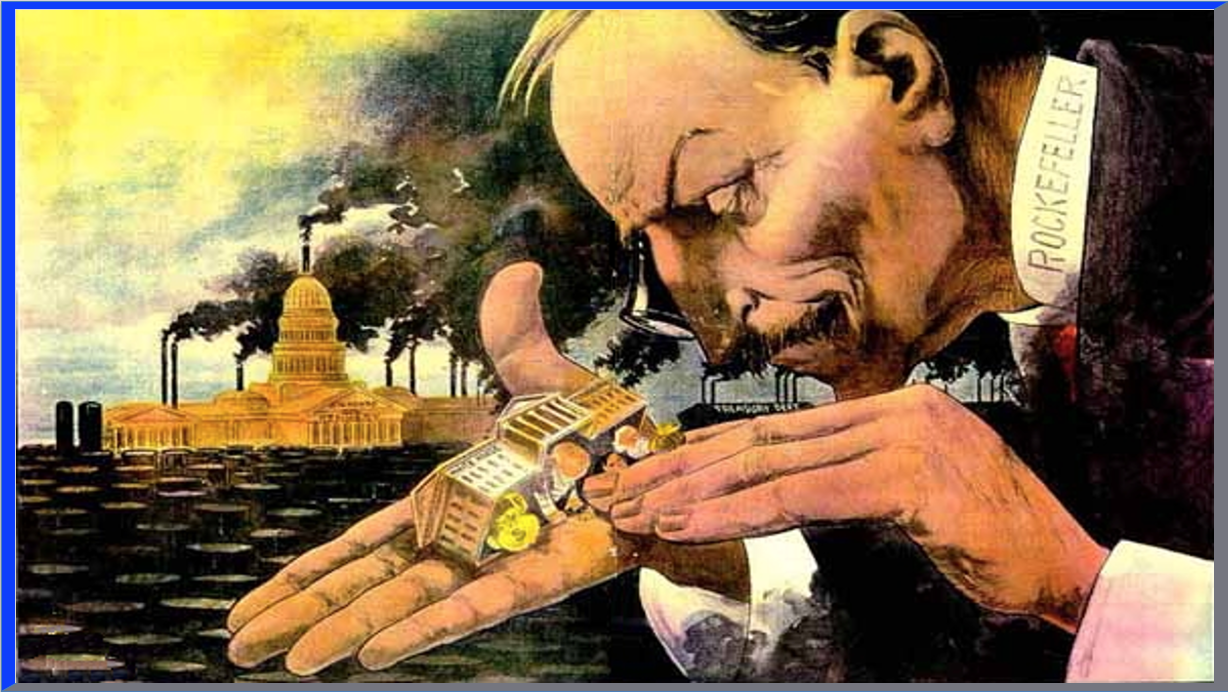
What is the role the government should play in the economy? That question has been present since the dawn of the nation with institutions like Hamilton’s National Bank or Clay’s American System which both saw the government play a major role in the economy. As the 20th century approached, that question is still in debate.
|
-
American History
- American History Honors >
- Unit 0: 1763 - 1800 - Revolutionary America
- Unit 1: 1800 - 1848 - Expansion & Reform
- Unit 2: 1848 - 1877 - A Nation Divided
- Unit 3: 1865 - 1898 - The Gilded Age
- Unit 4: 1890 - 1920 - American World Debut
- Unit 5: 1920 - 1945 - Trials and Tribulations
- Unit 6: 1945 - 1963 - Cold War Tensions
- Unit 7: 1955 - 1980 - Conflicts & Resolutions
- Unit 8: 1980 - present - Modern America
-
World History
- World History Honors
- Unit 1: (1200-1450) - State Building in the Global Tapestry
- Unit 2: (1200-1450) - Networks of Exchange
- Unit 3: (1450-1750) - Land-Based Empires
- Unit 4: (1450-1750) - Sea of Exploration
- Unit 5: (1750-1900) - Revolutions
- Unit 6: (1750-1900) - Imperial Migration
- Unit 7: (1900-present) - Global Conflicts
- Unit 8: (1900-present) - Cold War & Decolonization
- Unit 9: (1900-present) - Globalization
-
Advanced Placement (AP)
-
AP World History
>
- Unit 1: (1200-1450) - State Building in the Global Tapestry
- Unit 2: (1200-1450) - Networks of Exchange
- Unit 3: (1450-1750) - Land-Based Empires
- Unit 4: (1450-1750) - Transoceanic Interconnections
- Unit 5: (1750-1900) - Revolutions
- Unit 6: (1750-1900) - Imperial Migration
- Unit 7: (1900-present) - Global Conflicts
- Unit 8: (1900-present) - Cold War & Decolonization
- Unit 9: (1900-present) - Globalization
-
AP European History
>
- Unit I - The Rise of Europe
- Unit II - Rebirth and Exploration
- Unit III - A Fractured Faith
- Unit IV - A Question of Sovereignty
- Unit V - A Shifting Society
- Unit VI - Revolution
- Unit VII - Political Turmoil
- Unit VIII - Rise of the Nation-State
- Unit IX - Forging the Modern Era
- Unit X - Imperialism and the Great War
- Unit XI - Global Conflicts
- Unit XII - The Long Peace
-
AP World History
>
- Civic Literacy