-
American History
- American History Honors >
- Unit 0: 1763 - 1800 - Revolutionary America
- Unit 1: 1800 - 1848 - Expansion & Reform
- Unit 2: 1848 - 1877 - A Nation Divided
- Unit 3: 1865 - 1898 - The Gilded Age
- Unit 4: 1890 - 1920 - American World Debut
- Unit 5: 1920 - 1945 - Trials and Tribulations
- Unit 6: 1945 - 1963 - Cold War Tensions
- Unit 7: 1955 - 1980 - Conflicts & Resolutions
- Unit 8: 1980 - present - Modern America
-
World History
- World History Honors
- Unit 1: (1200-1450) - State Building in the Global Tapestry
- Unit 2: (1200-1450) - Networks of Exchange
- Unit 3: (1450-1750) - Land-Based Empires
- Unit 4: (1450-1750) - Sea of Exploration
- Unit 5: (1750-1900) - Revolutions
- Unit 6: (1750-1900) - Imperial Migration
- Unit 7: (1900-present) - Global Conflicts
- Unit 8: (1900-present) - Cold War & Decolonization
- Unit 9: (1900-present) - Globalization
-
Advanced Placement (AP)
-
AP World History
>
- Unit 1: (1200-1450) - State Building in the Global Tapestry
- Unit 2: (1200-1450) - Networks of Exchange
- Unit 3: (1450-1750) - Land-Based Empires
- Unit 4: (1450-1750) - Transoceanic Interconnections
- Unit 5: (1750-1900) - Revolutions
- Unit 6: (1750-1900) - Imperial Migration
- Unit 7: (1900-present) - Global Conflicts
- Unit 8: (1900-present) - Cold War & Decolonization
- Unit 9: (1900-present) - Globalization
-
AP European History
>
- Unit I - The Rise of Europe
- Unit II - Rebirth and Exploration
- Unit III - A Fractured Faith
- Unit IV - A Question of Sovereignty
- Unit V - A Shifting Society
- Unit VI - Revolution
- Unit VII - Political Turmoil
- Unit VIII - Rise of the Nation-State
- Unit IX - Forging the Modern Era
- Unit X - Imperialism and the Great War
- Unit XI - Global Conflicts
- Unit XII - The Long Peace
-
AP World History
>
- Civic Literacy
|
NEED TO KNOW
|
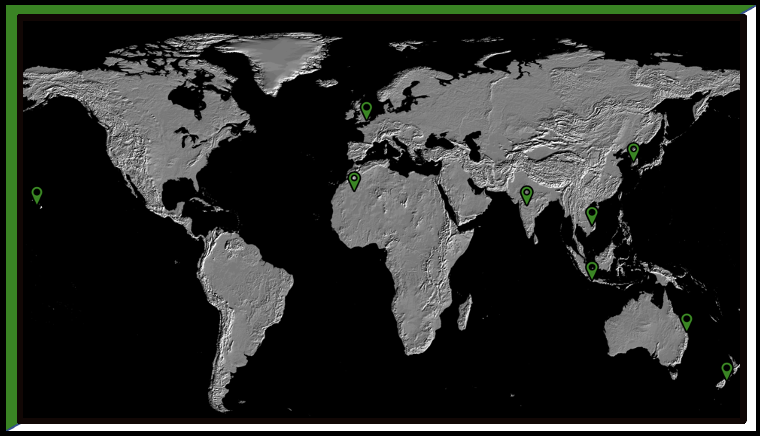
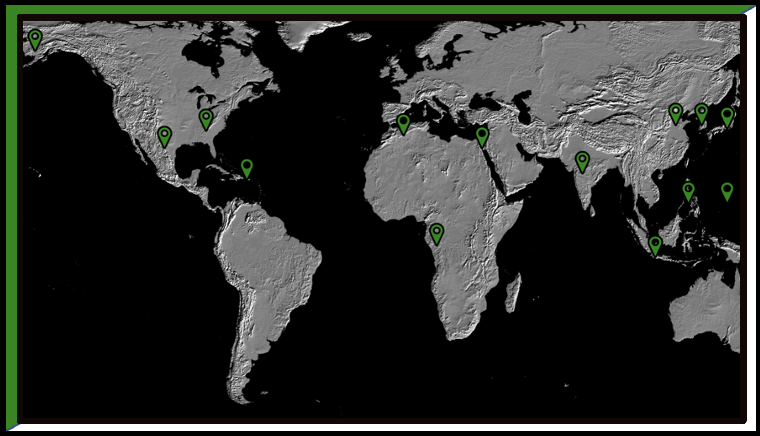
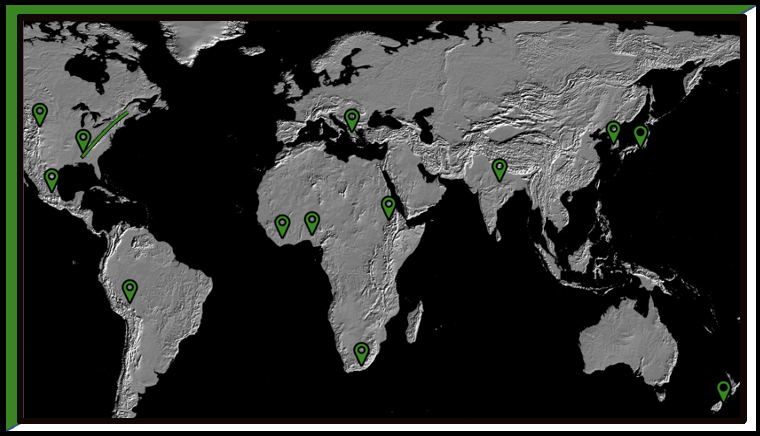
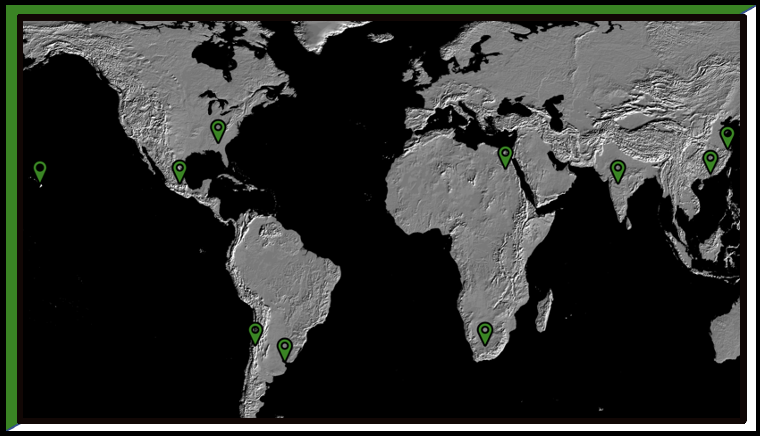
Imperial expansion began in the mid-18th century with the nations exploiting foreign lands for profit without directly taking territory but cooperating with local rulers. Due to the failings of colonization throughout the 19th century, many states began directly conquering most of Africa and Southeast Asia in the Age of Imperialism.
|
|
NEED TO KNOW
|
Due to the failings of colonization in the Americas throughout the early 19th century, many states began directly conquering most of Africa and Southeast Asia in a new wave of imperialism that swept whole continents under foreign control with Europeans dominating the era.
|
|
NEED TO KNOW
|
As industrial nations swept across the globe attempting to expand their empires by conquering new territories, the native population in those conquered territories typically resented foreign encroachment and resisted this expansion whenever possible fostering a rise in nationalism among native populations and uniting them against imperial powers.
|
|
NEED TO KNOW
|
Imperial empires needed raw materials and resources drawn from their imperial holdings as well as markets to sell their industrial manufactured goods. Therefore, economics was the largest driver of imperialism because, without a source of profit for the imperial empires, there would be no need to imperialize in the first place.
|
|
NEED TO KNOW
|
Economies had been globalized by the Industrial Revolution due to economic imperialism or new modes of transportation like steamships and railroads. This led to the mass migration of people worldwide and impacted the new homes they made in foreign lands.
|
-
American History
- American History Honors >
- Unit 0: 1763 - 1800 - Revolutionary America
- Unit 1: 1800 - 1848 - Expansion & Reform
- Unit 2: 1848 - 1877 - A Nation Divided
- Unit 3: 1865 - 1898 - The Gilded Age
- Unit 4: 1890 - 1920 - American World Debut
- Unit 5: 1920 - 1945 - Trials and Tribulations
- Unit 6: 1945 - 1963 - Cold War Tensions
- Unit 7: 1955 - 1980 - Conflicts & Resolutions
- Unit 8: 1980 - present - Modern America
-
World History
- World History Honors
- Unit 1: (1200-1450) - State Building in the Global Tapestry
- Unit 2: (1200-1450) - Networks of Exchange
- Unit 3: (1450-1750) - Land-Based Empires
- Unit 4: (1450-1750) - Sea of Exploration
- Unit 5: (1750-1900) - Revolutions
- Unit 6: (1750-1900) - Imperial Migration
- Unit 7: (1900-present) - Global Conflicts
- Unit 8: (1900-present) - Cold War & Decolonization
- Unit 9: (1900-present) - Globalization
-
Advanced Placement (AP)
-
AP World History
>
- Unit 1: (1200-1450) - State Building in the Global Tapestry
- Unit 2: (1200-1450) - Networks of Exchange
- Unit 3: (1450-1750) - Land-Based Empires
- Unit 4: (1450-1750) - Transoceanic Interconnections
- Unit 5: (1750-1900) - Revolutions
- Unit 6: (1750-1900) - Imperial Migration
- Unit 7: (1900-present) - Global Conflicts
- Unit 8: (1900-present) - Cold War & Decolonization
- Unit 9: (1900-present) - Globalization
-
AP European History
>
- Unit I - The Rise of Europe
- Unit II - Rebirth and Exploration
- Unit III - A Fractured Faith
- Unit IV - A Question of Sovereignty
- Unit V - A Shifting Society
- Unit VI - Revolution
- Unit VII - Political Turmoil
- Unit VIII - Rise of the Nation-State
- Unit IX - Forging the Modern Era
- Unit X - Imperialism and the Great War
- Unit XI - Global Conflicts
- Unit XII - The Long Peace
-
AP World History
>
- Civic Literacy